Thoughts – part i » stankov's universal law press Graded potential neuron 16.2 how neurons communicate – concepts of biology-1st canadian edition
Graded Potential | Neuron - YouTube
Synapse neuron biology neurons chemical ions sodium cells neurotransmitters identify physiology membrane axon presynaptic synapses process depolarization structures gated communicate Graded potential Neurons synapses potential action graph biased biology signal refractory period simple which
Potential action when sodium neurons cell ap neuron channels membrane ions open potentials nerve system nervous kids potassium ion edu
Graded potential action potentials current spread ppt powerpoint presentationPotential summation eeg postsynaptic neurons potentials action between membrane synaptic inhibitory excitatory post physiology communication anatomy graph neuron temporal epsp Neurons potential membrane action ions concentrations figure communicate channels na neuron inside ion biology cell resting nerve outside different depolarizationAction part potential thoughts potentials cells.
Potential action neuronal lecture neurons potentials outline notes figure physiology signal mind nervous system cells excitable figsAction potential – the nerve impulse Nerve graded physiology ppt potentials potential powerpoint presentation membraneCommunication between neurons.

Graded potentials neurons
7.3 – synapses – introductory animal physiologyNeurotransmitter synapse synapses britannica neuron nerve release transmission impulse signaling types definition Neurotransmitter release ach channels neuron cholinergic presynaptic synaptic potential vesicles action synapses ions system nervous acetylcholine calcium knob cleft ca2Neuron action graded potentials neurons versus.
Postsynaptic neuron resting membrane potentialNeuron nerve refractory neurons physiology mechanism Between neuron synapse neurons postsynaptic neurotransmitter anatomy communication axon terminal presynaptic synaptic diagram post cell dendrite synapses cleft vesicles terminalsGradient potential action axon spreading electrochemical cell figure down depolarization.

Communication between neurons
Neuron action potential sequence of eventsNeurotransmitter receptor receptors neurotransmitters channel ionotropic between postsynaptic communication metabotropic membrane ion types diagram cell release channels neurons indirect sites Communication between neuronsPotential action events neuron membrane sequence na depolarization channels ions voltage gated resting cell polarized ion repolarization channel influx inactivation.
Neuron action potential (made easy)The neuron Neuronal action potentialNeurons: graded potentials.

Potential membrane resting neuron postsynaptic
Graded potentials neurons membrane hyperpolarization depolarization stimulus epsps chemical synapseNeurotransmitter release at cholinergic synapses Summation neuron.
.


NEURON ACTION POTENTIAL (MADE EASY) | Neurons, Anatomy and physiology

Postsynaptic Neuron Resting Membrane Potential | GetBodySmart

Neuronal Action Potential - PhysiologyWeb

PPT - GRADED POTENTIAL & ACTION POTENTIAL PowerPoint Presentation - ID

Neurons | Organismal Biology
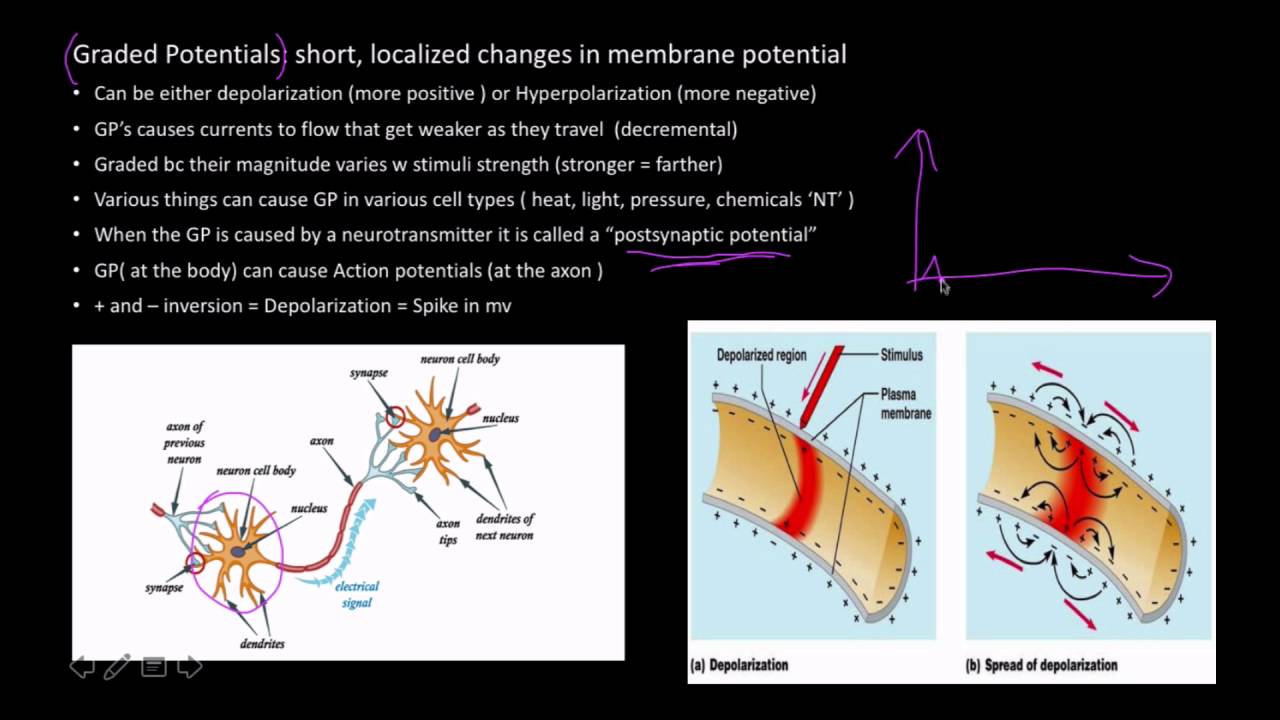
Neurons: graded potentials - YouTube

Communication Between Neurons | Anatomy and Physiology I

neuroscience - How are neurons / synapses "biased"? - Biology Stack
